
According to a recent survey by the McKinsey Health Institute, social media engagement among Gen Z can have both positive and negative impacts on their mental health, including finding support and connection.
Similar to other relationships in the age range of 18 to 24, the bond between a young person and social media can be complex. A recent global survey revealed that social media usage can induce fear of missing out (FOMO) or negative body image, but it can also assist in fostering social connections and self-expression, regardless of their location.
The 2022 Global Gen Z Survey by McKinsey Health Institute (MHI) surveyed over 42,000 individuals in 26 countries on various aspects of health, including mental, physical, social, and spiritual dimensions. The goal was to analyze differences and similarities across generations and countries to shed light on Gen Z mental health.

The Complex Relationship Between Gen Z and Social Media
According to the McKinsey Health Institute’s 2022 Global Gen Z Survey, Gen Zers tend to have more negative feelings towards social media and report poorer mental health compared to other generations. However, the relationship between social media use and mental health is complex, and positive effects were also reported. Older generations were found to engage with social media platforms as much as Gen Zers.
The survey also revealed that technology provides access to support mental health resources for younger people, with Gen Zers more likely to use digital wellness apps and mental health programs. Additionally, social media use can benefit mental health in some cases, such as using it for self-expression. Young refugees and asylum seekers are among those who use social media to stay connected and decrease loneliness.
Variations in Mental Health among Generations Globally
A recent survey conducted by McKinsey Health Institute shows that there are significant differences in mental health experiences within and between generations globally. While one in seven baby boomers reported a decline in their mental health, one in four Gen Z respondents reported poor mental health over the past three years. Moreover, female Gen Zers were nearly twice as likely as their male counterparts to report poor mental health.
The study found that in most surveyed countries, Gen Z participants reported struggling with their mental health the most compared to other dimensions of health. However, in some countries, including China, Egypt, Nigeria, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and Vietnam, social health was reported as the most challenging for Gen Z. The study notes that the causes of poor mental health among Gen Z are not yet clear, and several factors, such as developmental stage and societal attitudes, may be influencing their mental health experiences.
Social Media Use Across Generations
Mental health experiences vary by region. The underlying cause is unclear, but age-specific factors may impact Gen Z’s mental health.
Social media is widely used by people of all ages, with over 75% of respondents reporting checking social media for at least ten minutes a day. Millennials are the most active users, with 32% posting daily or multiple times a day.
Although younger generations, such as Gen Z, engage with social media regularly, they are less likely to post and spend more time passively scrolling. However, the effects of passive social media use on subjective well-being are still debated.
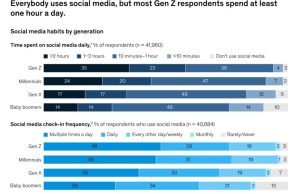
Source: McKinsey Health Institute
The Complex Relationship Between Social Media Use and Mental Health in Young Adults
Studies have indicated that increased screen time is associated with poorer psychological well-being in young adults. However, recent research suggests that the nature of one’s relationship with social media can have a greater impact on mental health than time spent.
While many respondents report positive effects of social media on mental health, negative impacts are most pronounced for Gen Zers spending more than two hours a day on social media and those with poor mental health. Additionally, regional differences in reported negative impacts exist, with European and Oceanian Gen Zers reporting the highest levels.
Leveraging Technology for Youth Mental Health Support
Social media and technology, often discussed in relation to youth mental health, can also be used as effective tools for promoting well-being and providing scalable mental health support. One potential way to do this is by incorporating algorithms into social media platforms to facilitate access to crisis hotlines, support groups, and emergency mental health services for youth expressing psychological distress.
Digital mental health companies could also collaborate with virtual and community-based providers to ensure timely and culturally-appropriate crisis services are available to those with high-acuity needs.
Final Words
The McKinsey Health Institute conducted a global survey of over 42,000 respondents across 26 countries to analyze the relationship between social media use and mental health in different age groups. The study found that Gen Z respondents were more likely to report the negative impacts of social media on their mental health compared to other age groups and that women in this age group were more likely to report poor mental health than men. However, there were also positive impacts reported by all age groups, such as self-expression and social connectivity.
The study suggests that developers could incorporate algorithms to help youth find mental health support and companies could partner with virtual and community-based providers to offer timely and culturally-appropriate crisis services.

